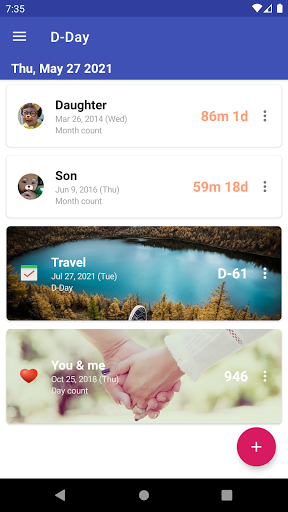
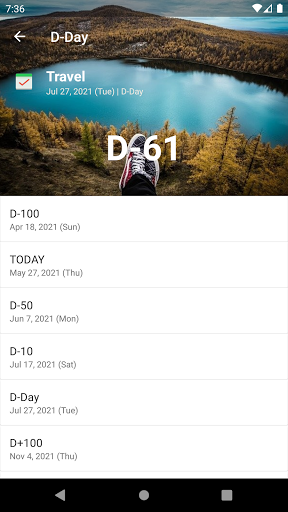
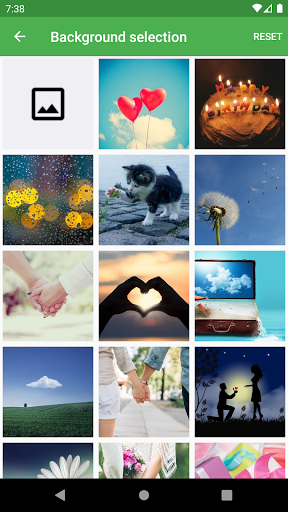
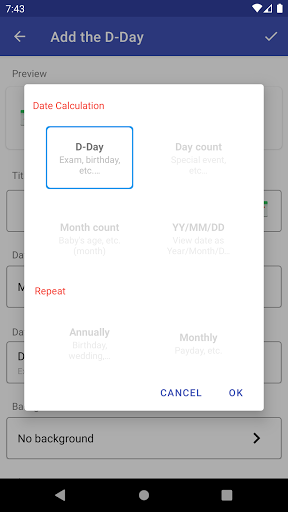
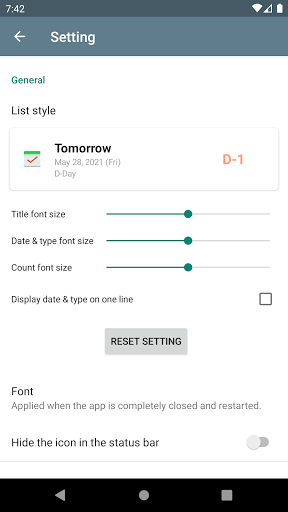
Simple d-day app.
- Add, edit, delete the D-Day
- Add the image to the D-Day.
- You can see it by the month.
- Simple widget, that allows you to show D-Day in your home screen.
Introduction
D-Day, the code name for the Allied invasion of Normandy, was a pivotal moment in World War II. Launched on June 6, 1944, the operation involved over 156,000 troops and 5,000 ships and landing craft. Its success marked a turning point in the war, leading to the liberation of Western Europe from Nazi Germany.
Background
After the Allies' successful invasion of North Africa in 1942, they began planning for a second front in Europe. The chosen target was Normandy, a strategically important region in northwestern France. The Allies hoped to gain a foothold on the continent and push back the German forces.
Planning and Preparations
The invasion plan, code-named Operation Overlord, was meticulously crafted over two years. It involved extensive deception and disinformation campaigns to mislead the Germans about the location and timing of the attack. Allied forces trained rigorously in preparation for the assault, practicing amphibious landings and beach operations.
The Landings
At dawn on June 6, 1944, Allied troops stormed the beaches of Normandy. The first wave of landings targeted five sectors: Utah, Omaha, Gold, Juno, and Sword. Each sector faced varying degrees of resistance from the German defenders.
Utah Beach
Utah Beach, the westernmost landing site, was the most successful. The 4th Infantry Division encountered relatively light resistance and quickly established a beachhead.
Omaha Beach
Omaha Beach, the most heavily defended sector, proved to be a bloody battleground. The 1st and 29th Infantry Divisions faced fierce German resistance and suffered heavy casualties.
Gold Beach
Gold Beach, targeted by the British 50th Infantry Division, saw moderate resistance. The troops secured the beachhead and linked up with the Canadian forces at Juno Beach.
Juno Beach
Juno Beach, the responsibility of the Canadian 3rd Infantry Division, also faced moderate resistance. The Canadians successfully established a beachhead and advanced inland.
Sword Beach
Sword Beach, the easternmost landing site, was assaulted by the British 3rd Infantry Division. They encountered strong German defenses but managed to gain a foothold on the beach.
Aftermath
The D-Day landings were a costly but ultimately successful operation. Allied forces gained a foothold in Normandy and began the liberation of Western Europe. The invasion paved the way for the subsequent advance into Germany and the eventual defeat of Nazi Germany.
Legacy
D-Day remains a significant event in world history. It marked a turning point in World War II and is remembered as a testament to the courage and sacrifice of the Allied forces. The landings have been commemorated in numerous films, books, and memorials, ensuring that the memory of this pivotal moment lives on.
Simple d-day app.
- Add, edit, delete the D-Day
- Add the image to the D-Day.
- You can see it by the month.
- Simple widget, that allows you to show D-Day in your home screen.
Introduction
D-Day, the code name for the Allied invasion of Normandy, was a pivotal moment in World War II. Launched on June 6, 1944, the operation involved over 156,000 troops and 5,000 ships and landing craft. Its success marked a turning point in the war, leading to the liberation of Western Europe from Nazi Germany.
Background
After the Allies' successful invasion of North Africa in 1942, they began planning for a second front in Europe. The chosen target was Normandy, a strategically important region in northwestern France. The Allies hoped to gain a foothold on the continent and push back the German forces.
Planning and Preparations
The invasion plan, code-named Operation Overlord, was meticulously crafted over two years. It involved extensive deception and disinformation campaigns to mislead the Germans about the location and timing of the attack. Allied forces trained rigorously in preparation for the assault, practicing amphibious landings and beach operations.
The Landings
At dawn on June 6, 1944, Allied troops stormed the beaches of Normandy. The first wave of landings targeted five sectors: Utah, Omaha, Gold, Juno, and Sword. Each sector faced varying degrees of resistance from the German defenders.
Utah Beach
Utah Beach, the westernmost landing site, was the most successful. The 4th Infantry Division encountered relatively light resistance and quickly established a beachhead.
Omaha Beach
Omaha Beach, the most heavily defended sector, proved to be a bloody battleground. The 1st and 29th Infantry Divisions faced fierce German resistance and suffered heavy casualties.
Gold Beach
Gold Beach, targeted by the British 50th Infantry Division, saw moderate resistance. The troops secured the beachhead and linked up with the Canadian forces at Juno Beach.
Juno Beach
Juno Beach, the responsibility of the Canadian 3rd Infantry Division, also faced moderate resistance. The Canadians successfully established a beachhead and advanced inland.
Sword Beach
Sword Beach, the easternmost landing site, was assaulted by the British 3rd Infantry Division. They encountered strong German defenses but managed to gain a foothold on the beach.
Aftermath
The D-Day landings were a costly but ultimately successful operation. Allied forces gained a foothold in Normandy and began the liberation of Western Europe. The invasion paved the way for the subsequent advance into Germany and the eventual defeat of Nazi Germany.
Legacy
D-Day remains a significant event in world history. It marked a turning point in World War II and is remembered as a testament to the courage and sacrifice of the Allied forces. The landings have been commemorated in numerous films, books, and memorials, ensuring that the memory of this pivotal moment lives on.