The New Testament, the Orthodox, Cornilescu, Catholic, Belgrade, Smyrna versions
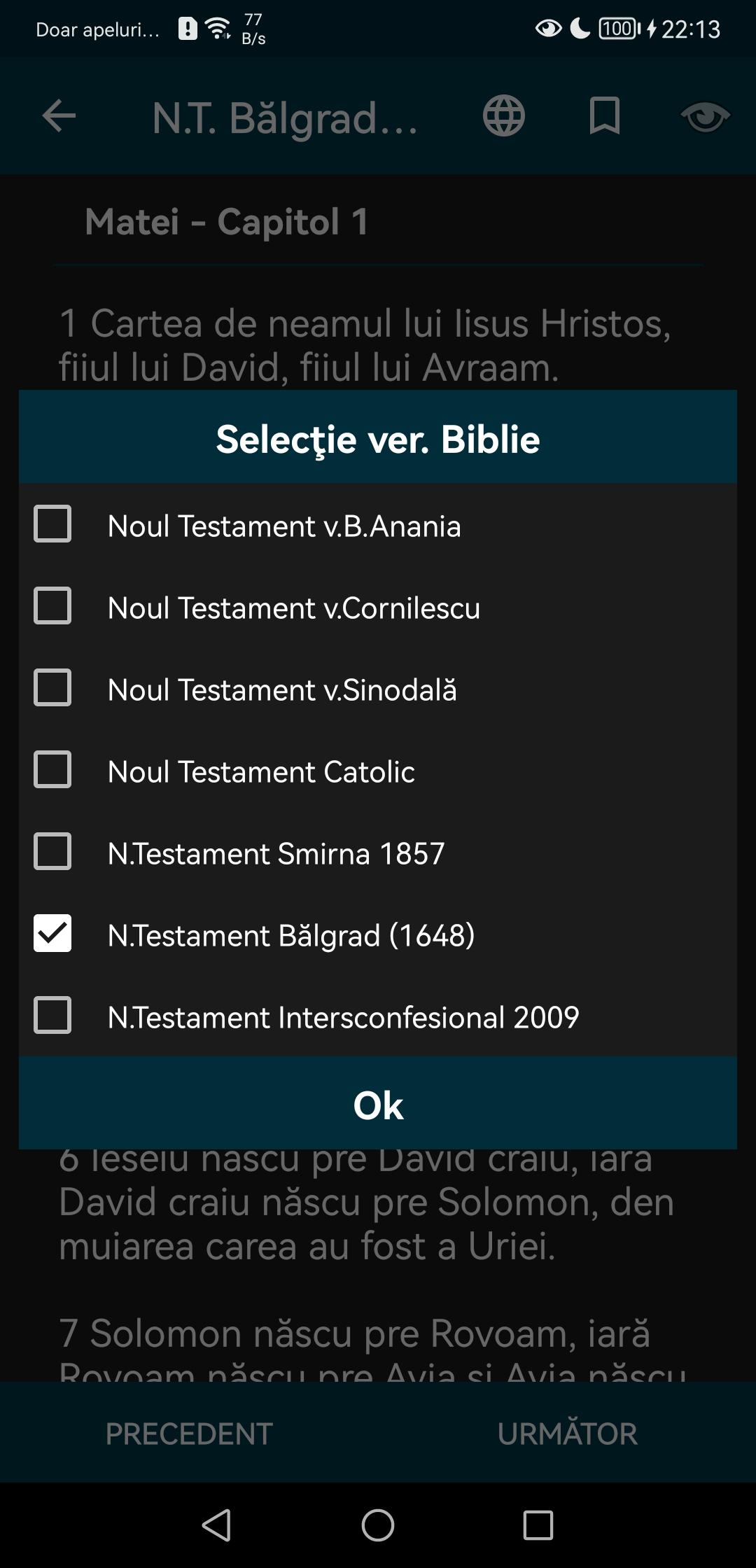
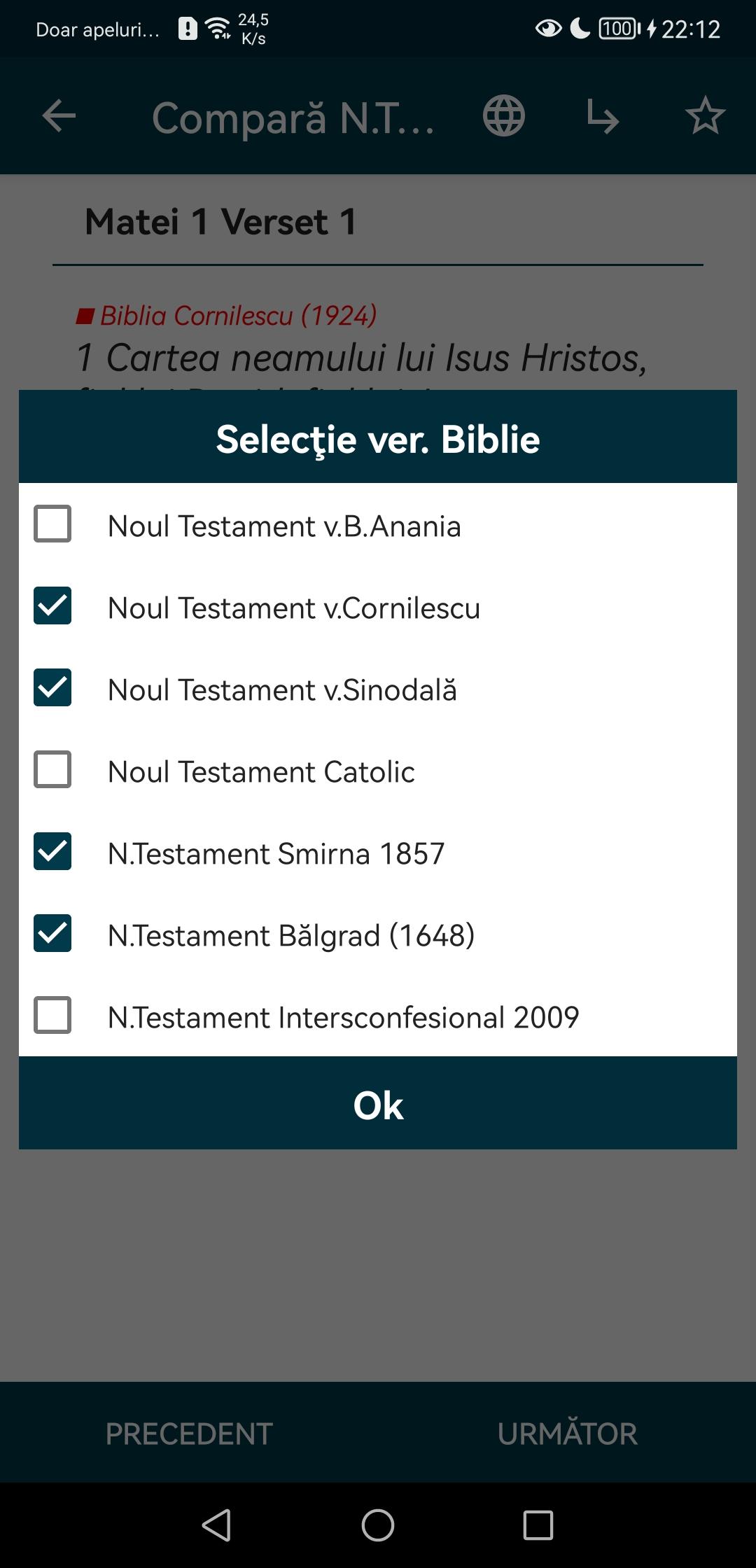
The application includes the following versions of the New Testament, the verses can be compared or you can read any version of them:
-Bible version Bartholomew Ananias (2001)
- Cornilescu's Bible (1924)
-Orthodox Synodal Bible (1982)
-Catholic Bible (2013)
-The New Testament from Smyrna (1857)
-New Testament from Belgrade (1648)
-The Interconfessional New Testament (2009)
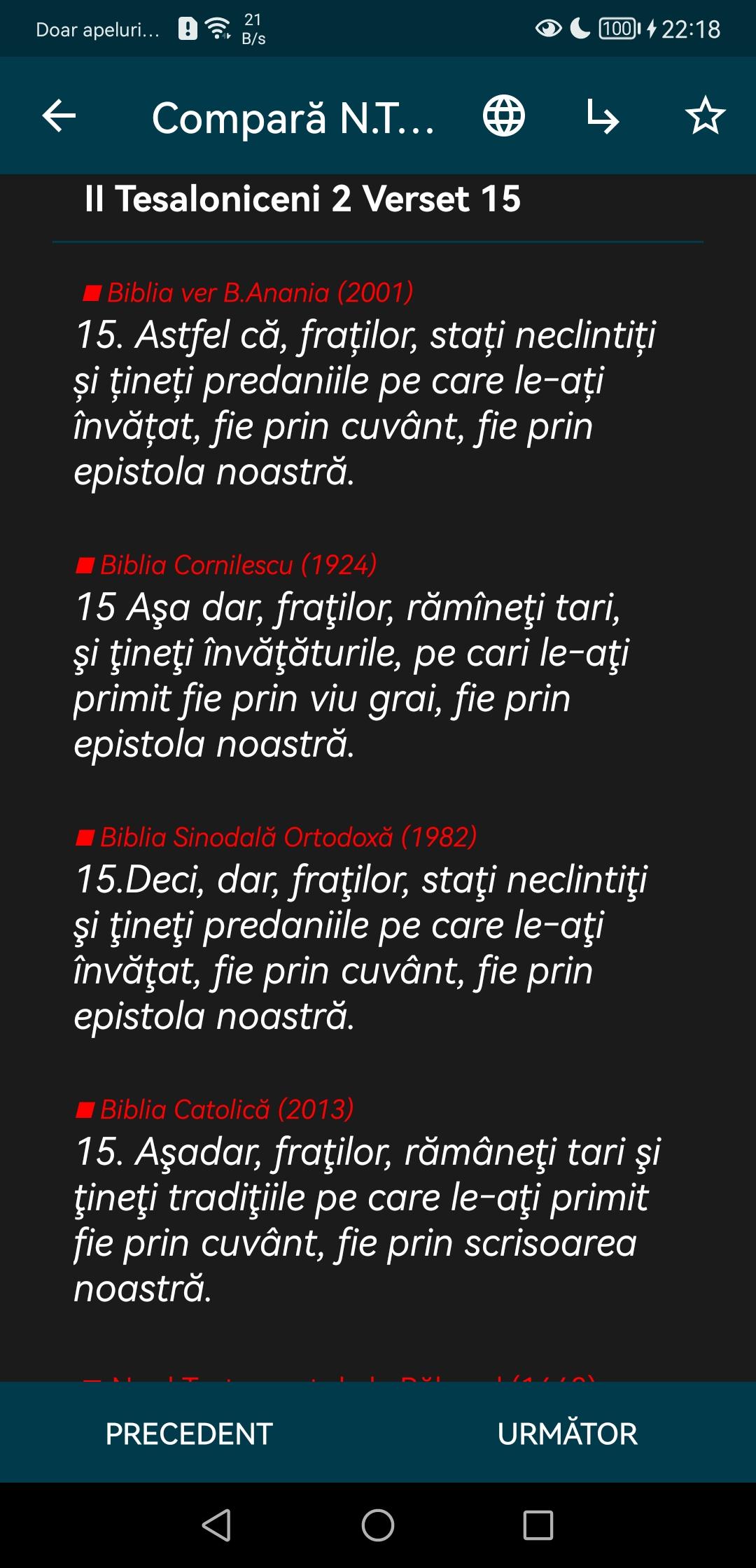
There are differences between the Protestant, Orthodox and Catholic Bibles. The translations of the Bibles are not identical because each individual Bible bears the significant imprint of the doctrine of the cult to which it belongs, also valid for the Orthodox Bible.
Example: 1 Corinthians 1:18. Orthodox: "For the word of the Cross, for those who perish, is madness; and for us, those who save ourselves, it is the power of God". Cornilescu: "Because the preaching of the cross is madness for those who are on the path of perdition, but for us, who are on the path of salvation, it is the power of God."
Catholic Bible: Indeed, the word of the cross is foolishness to those who are perishing, but to us who are being saved, it is the power of God.
While in the Orthodox translation "salvation" has a meaning that implies a vigil, a struggle throughout life, in Cornilescu's translation we read about Christians that "they are saved" or "they are already on the path of salvation", in the spirit of the neo-Protestant teaching that salvation is completed, that it has a precise calendar date in the believer's life and that it is certain. Based on a prayer of acceptance of the Saviour's sacrifice, man would have Heaven assured.
This offline app allows you to compare verses or read either version, has dark mode and indicator to mark where you left off with the reading.
Content
Noul Testament, a Romanian phrase translating to "New Testament," lacks a specific, identifiable game. The term likely refers to a fan-made mod, a localized version of a religious-themed game, or perhaps a misremembered title. Therefore, a comprehensive summary based on gameplay is impossible. Instead, this response explores potential interpretations and the broader context of religion in video games.
One possibility is a modification for an existing game, incorporating New Testament narratives. Numerous games lend themselves to such modifications, particularly open-world sandboxes or role-playing games. Imagine a mod for a game like Mount & Blade, transforming the medieval setting into a representation of Roman Judea. Players could potentially follow the life of Jesus, participate in biblical events, or even create alternative historical narratives. Such a mod could focus on historical accuracy, aiming to recreate the time period and its social structures. Alternatively, it could lean into more fantastical interpretations, incorporating miracles and supernatural elements.
Another interpretation considers Noul Testament as a localized version of a pre-existing religious game. Several games explore biblical themes, ranging from educational titles to more complex narratives. A Romanian localization of such a game would naturally adopt the title "Noul Testament" if its content focused on the New Testament scriptures. These games often feature simplified gameplay mechanics, focusing on conveying biblical stories and teachings. They might involve quizzes, interactive narratives, or even virtual tours of biblical locations.
The ambiguity of the term also opens up the possibility of a misremembered or misunderstood title. Perhaps the intended game was "The Testament," a series of action-adventure games with supernatural themes. While not directly related to the New Testament, the similarity in titles could lead to confusion. Alternatively, the intended game could be a lesser-known title dealing with biblical themes, its name lost to the passage of time or regional variations.
Regardless of the specific game, the presence of religious themes in video games is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon. Games can serve as a platform for exploring religious narratives, offering interactive experiences that engage players with biblical stories and characters. They can also be used for educational purposes, teaching players about religious history, beliefs, and practices. However, the depiction of religion in games can also be controversial, raising questions about accuracy, sensitivity, and the potential for misinterpretation.
The use of religious themes in games often sparks debate. Some argue that games can trivialize sacred texts or misrepresent religious beliefs. Others see the potential for games to foster understanding and dialogue across different faiths and perspectives. The interpretation of religious themes in games is ultimately subjective, influenced by the player's own beliefs and experiences.
The lack of concrete information about "Noul Testament" highlights the vast and ever-evolving landscape of video games. From fan-made modifications to localized versions and obscure titles, the world of gaming is filled with hidden gems and forgotten treasures. While the specific game remains a mystery, the exploration of its potential interpretations offers a glimpse into the diverse ways religion can intersect with the interactive medium of video games. Whether used for education, entertainment, or exploration, religious themes in games continue to spark discussion and offer unique perspectives on ancient narratives.
The New Testament, the Orthodox, Cornilescu, Catholic, Belgrade, Smyrna versions
The application includes the following versions of the New Testament, the verses can be compared or you can read any version of them:
-Bible version Bartholomew Ananias (2001)
- Cornilescu's Bible (1924)
-Orthodox Synodal Bible (1982)
-Catholic Bible (2013)
-The New Testament from Smyrna (1857)
-New Testament from Belgrade (1648)
-The Interconfessional New Testament (2009)
There are differences between the Protestant, Orthodox and Catholic Bibles. The translations of the Bibles are not identical because each individual Bible bears the significant imprint of the doctrine of the cult to which it belongs, also valid for the Orthodox Bible.
Example: 1 Corinthians 1:18. Orthodox: "For the word of the Cross, for those who perish, is madness; and for us, those who save ourselves, it is the power of God". Cornilescu: "Because the preaching of the cross is madness for those who are on the path of perdition, but for us, who are on the path of salvation, it is the power of God."
Catholic Bible: Indeed, the word of the cross is foolishness to those who are perishing, but to us who are being saved, it is the power of God.
While in the Orthodox translation "salvation" has a meaning that implies a vigil, a struggle throughout life, in Cornilescu's translation we read about Christians that "they are saved" or "they are already on the path of salvation", in the spirit of the neo-Protestant teaching that salvation is completed, that it has a precise calendar date in the believer's life and that it is certain. Based on a prayer of acceptance of the Saviour's sacrifice, man would have Heaven assured.
This offline app allows you to compare verses or read either version, has dark mode and indicator to mark where you left off with the reading.
Content
Noul Testament, a Romanian phrase translating to "New Testament," lacks a specific, identifiable game. The term likely refers to a fan-made mod, a localized version of a religious-themed game, or perhaps a misremembered title. Therefore, a comprehensive summary based on gameplay is impossible. Instead, this response explores potential interpretations and the broader context of religion in video games.
One possibility is a modification for an existing game, incorporating New Testament narratives. Numerous games lend themselves to such modifications, particularly open-world sandboxes or role-playing games. Imagine a mod for a game like Mount & Blade, transforming the medieval setting into a representation of Roman Judea. Players could potentially follow the life of Jesus, participate in biblical events, or even create alternative historical narratives. Such a mod could focus on historical accuracy, aiming to recreate the time period and its social structures. Alternatively, it could lean into more fantastical interpretations, incorporating miracles and supernatural elements.
Another interpretation considers Noul Testament as a localized version of a pre-existing religious game. Several games explore biblical themes, ranging from educational titles to more complex narratives. A Romanian localization of such a game would naturally adopt the title "Noul Testament" if its content focused on the New Testament scriptures. These games often feature simplified gameplay mechanics, focusing on conveying biblical stories and teachings. They might involve quizzes, interactive narratives, or even virtual tours of biblical locations.
The ambiguity of the term also opens up the possibility of a misremembered or misunderstood title. Perhaps the intended game was "The Testament," a series of action-adventure games with supernatural themes. While not directly related to the New Testament, the similarity in titles could lead to confusion. Alternatively, the intended game could be a lesser-known title dealing with biblical themes, its name lost to the passage of time or regional variations.
Regardless of the specific game, the presence of religious themes in video games is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon. Games can serve as a platform for exploring religious narratives, offering interactive experiences that engage players with biblical stories and characters. They can also be used for educational purposes, teaching players about religious history, beliefs, and practices. However, the depiction of religion in games can also be controversial, raising questions about accuracy, sensitivity, and the potential for misinterpretation.
The use of religious themes in games often sparks debate. Some argue that games can trivialize sacred texts or misrepresent religious beliefs. Others see the potential for games to foster understanding and dialogue across different faiths and perspectives. The interpretation of religious themes in games is ultimately subjective, influenced by the player's own beliefs and experiences.
The lack of concrete information about "Noul Testament" highlights the vast and ever-evolving landscape of video games. From fan-made modifications to localized versions and obscure titles, the world of gaming is filled with hidden gems and forgotten treasures. While the specific game remains a mystery, the exploration of its potential interpretations offers a glimpse into the diverse ways religion can intersect with the interactive medium of video games. Whether used for education, entertainment, or exploration, religious themes in games continue to spark discussion and offer unique perspectives on ancient narratives.