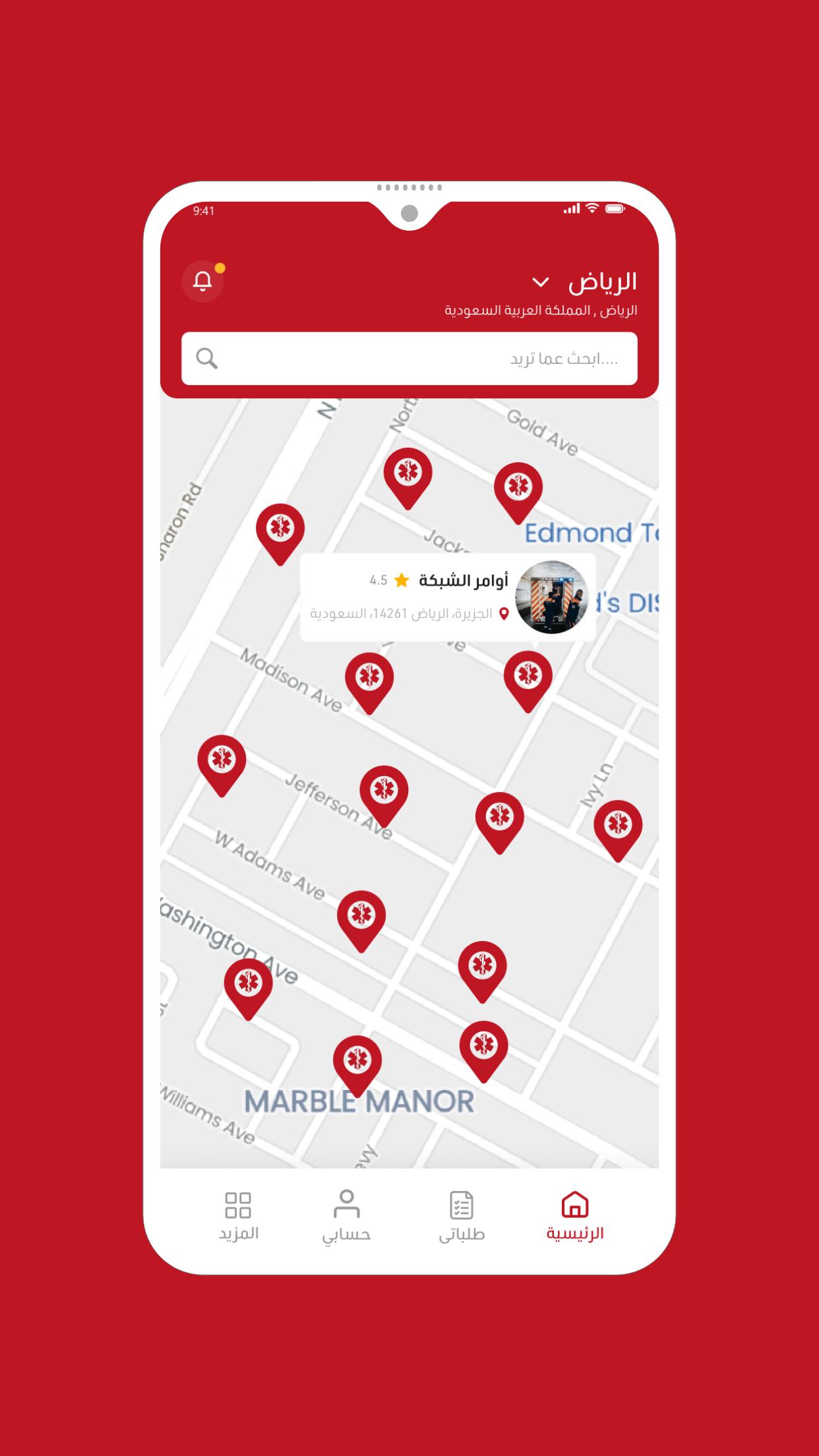
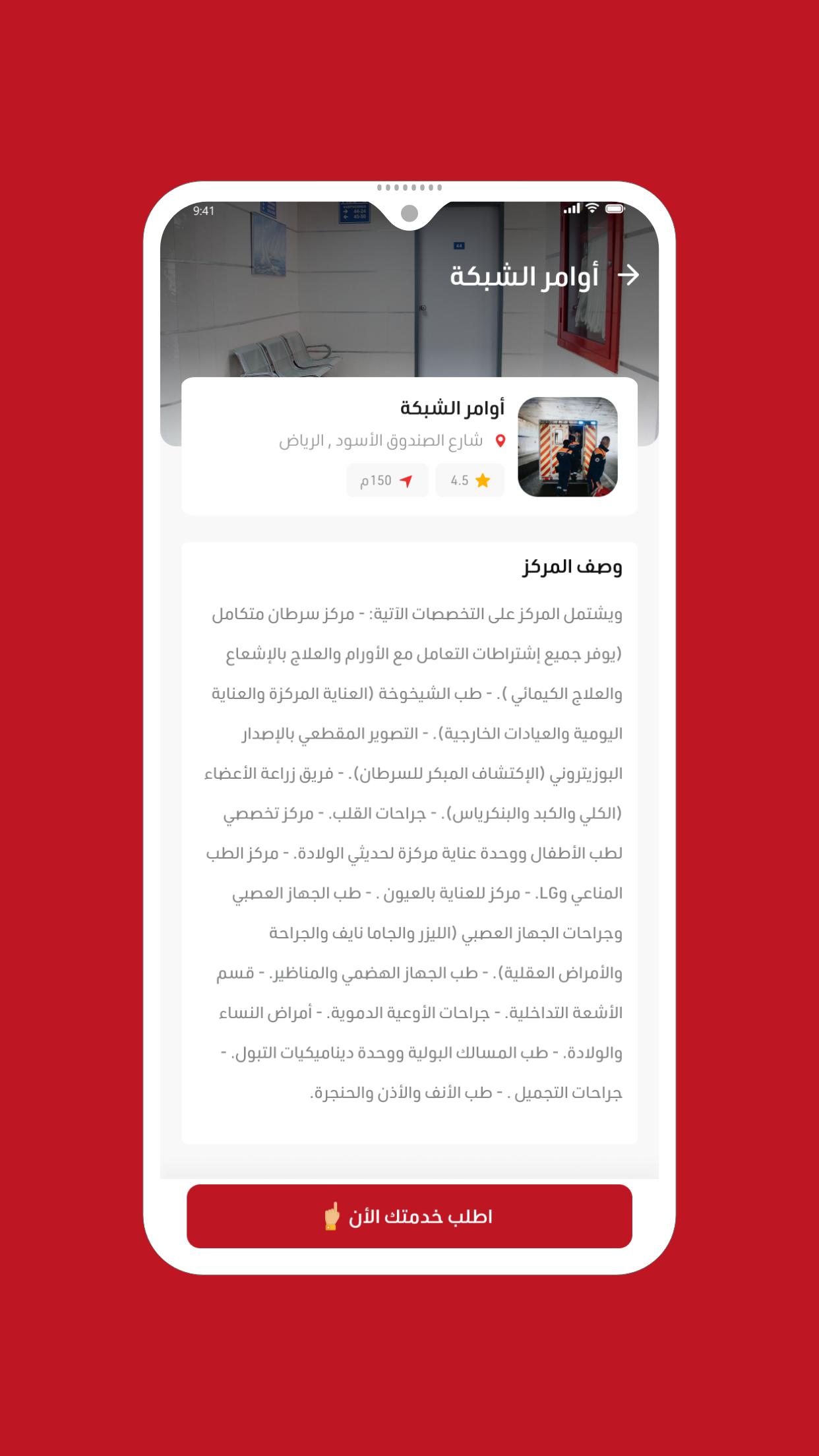
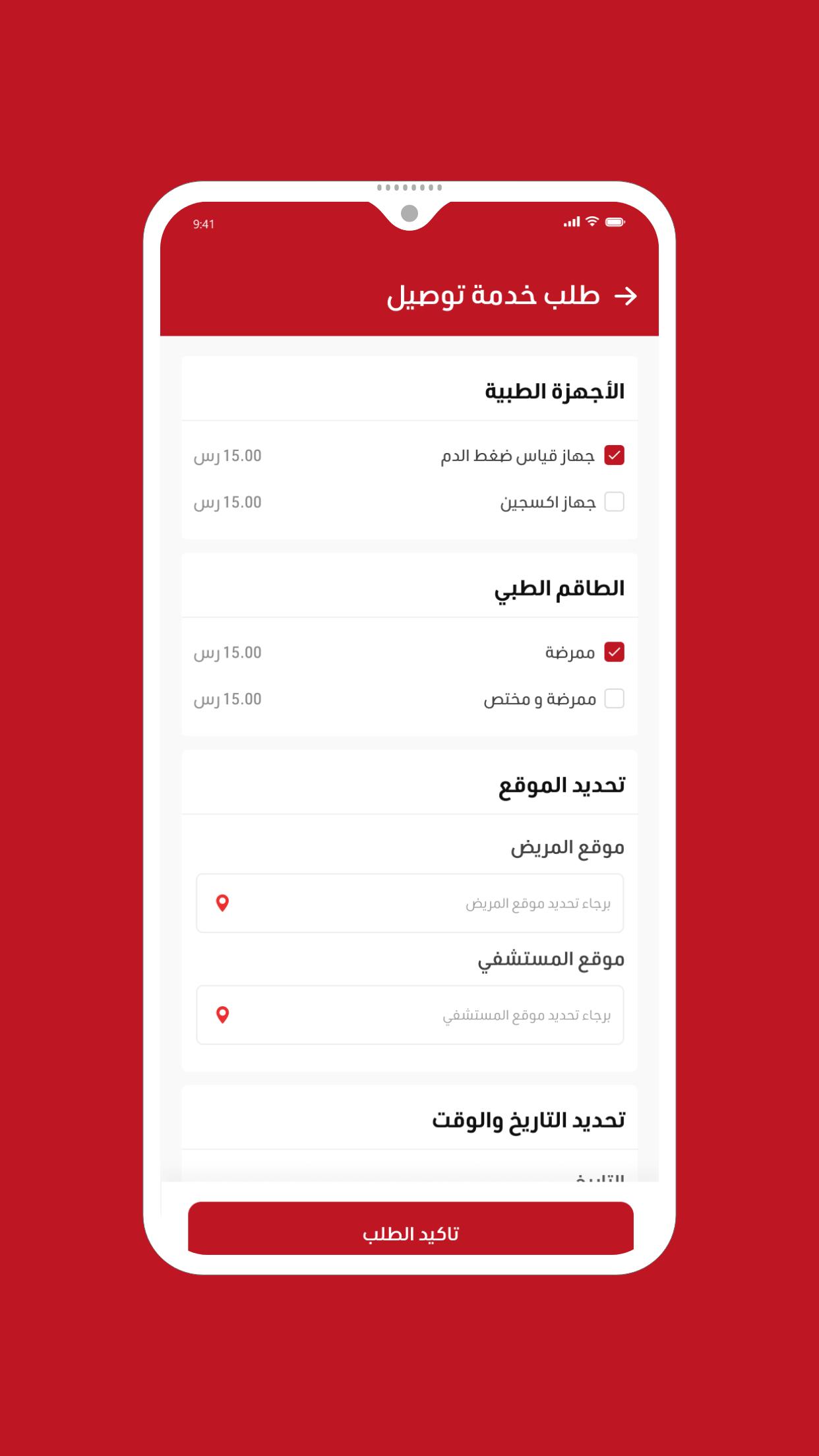
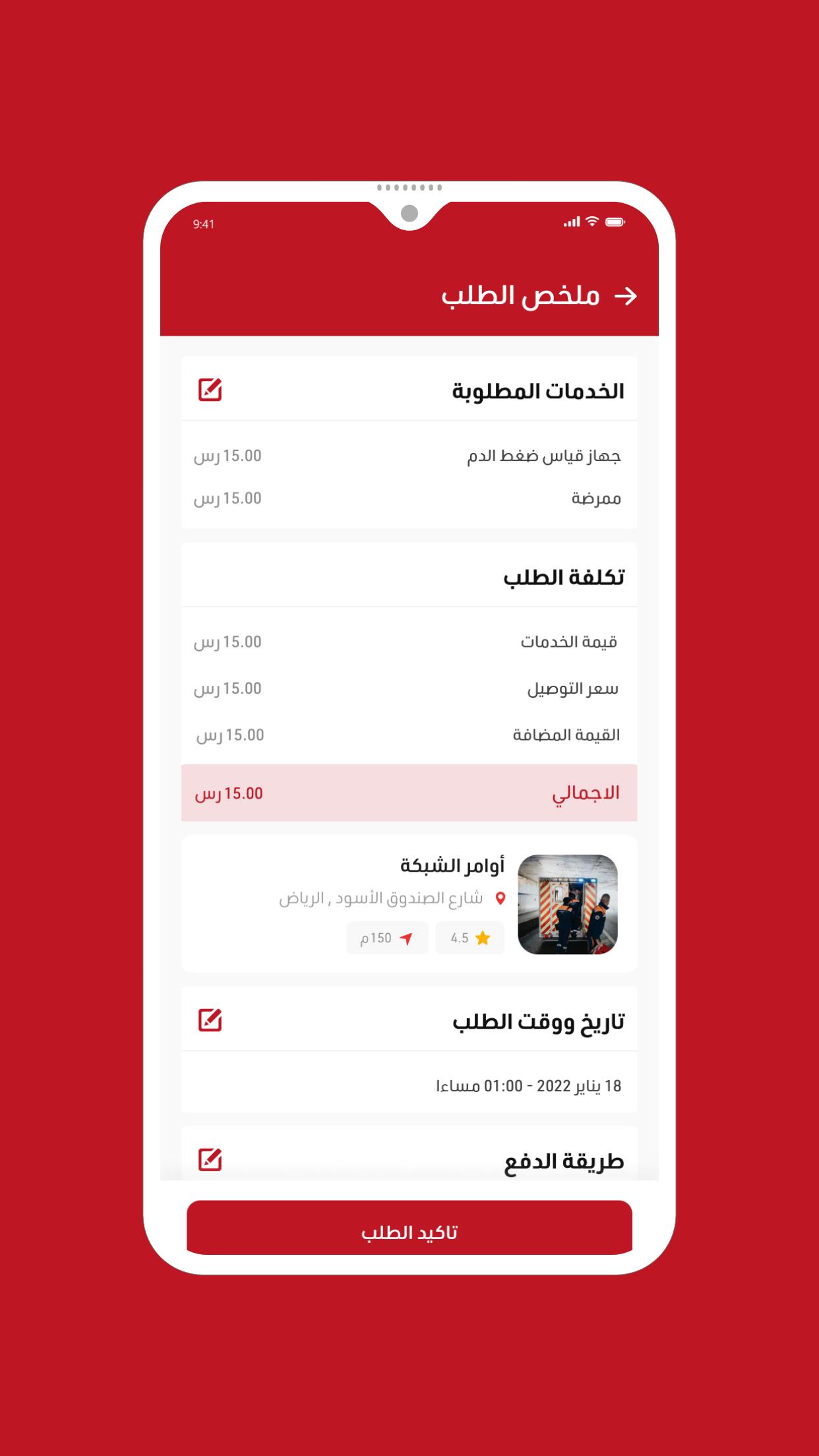
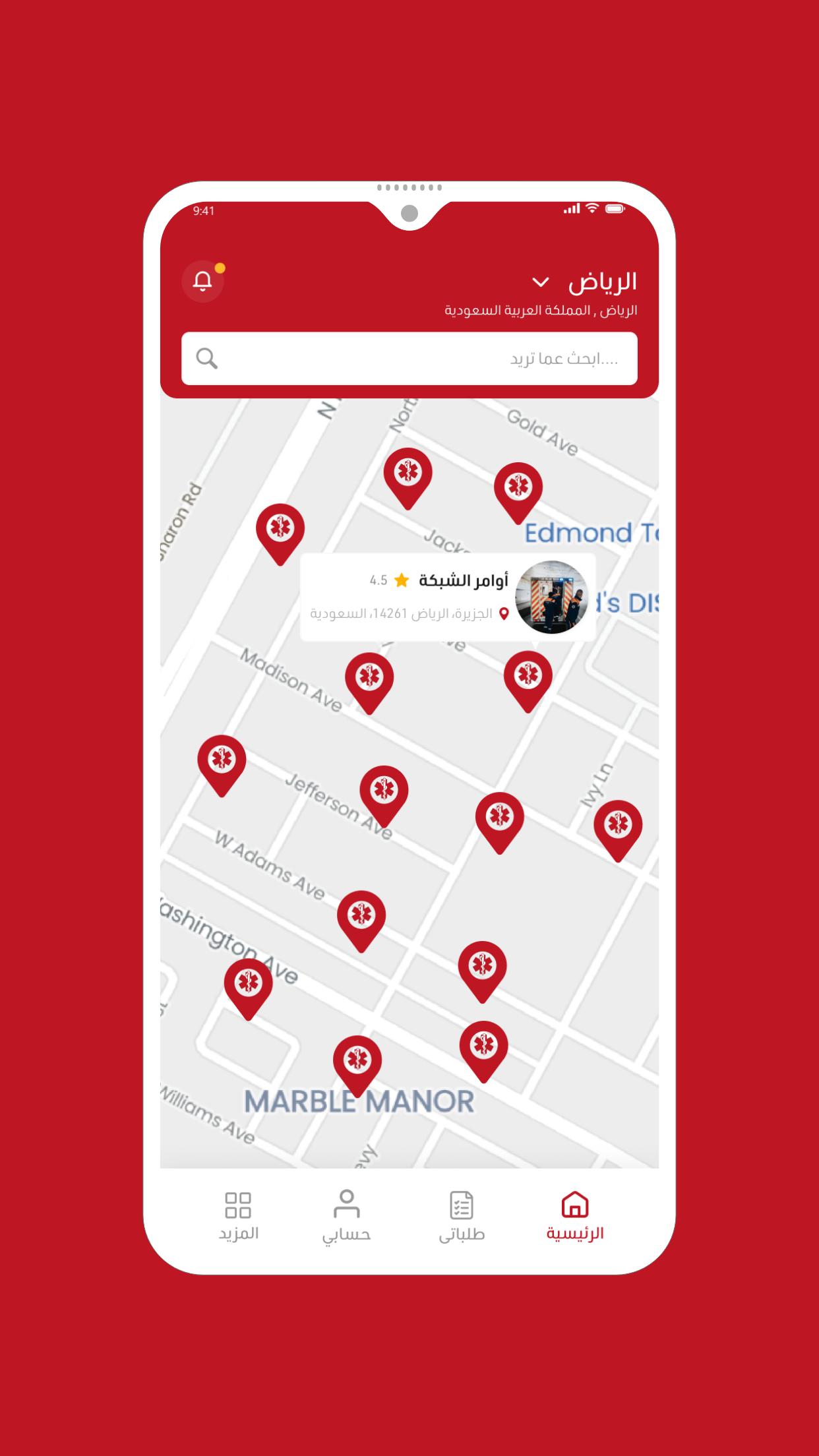
Comprehensive medical application
An application that connects patients with ambulance transport companies and hospitals
What's New in the Latest Version 1.0.8
Last updated on Jul 5, 2024
Minor bug fixes and improvements. Install or update to the newest version to check it out!
RRT: Rapidly Exploring Random TreesIntroduction
Rapidly Exploring Random Trees (RRT) is a sampling-based motion planning algorithm that constructs a tree-like data structure to explore a high-dimensional configuration space. It is commonly used in robotics to find collision-free paths for robot manipulators in complex environments.
Algorithm
The RRT algorithm iteratively constructs a tree rooted at the starting configuration. At each iteration, it:
1. Random Sampling: Randomly sample a point in the configuration space.
2. Nearest Neighbor: Find the nearest node in the tree to the sampled point.
3. Extension: Extend the tree towards the sampled point by a small step in the direction of the nearest neighbor.
4. Collision Check: Check if the new node is in collision with obstacles. If not, add it to the tree.
Advantages
* Asymptotically Complete: RRT is asymptotically complete, meaning it will eventually find a path to the goal if one exists.
* Sampling-Based: It does not require explicit knowledge of the environment's geometry.
* Incremental: The tree is constructed incrementally, allowing for real-time path planning.
* Easily Parallelizable: The algorithm can be parallelized to improve computational efficiency.
Limitations
* High Computational Cost: RRT can be computationally expensive for high-dimensional configuration spaces.
* Trapping in Local Minima: The algorithm may get trapped in local minima, leading to suboptimal paths.
* Non-Optimal Solutions: RRT does not guarantee the optimality of the found path.
Variants
Several variants of RRT have been developed to address its limitations:
* RRT-Connect: Connects two RRTs from the start and goal configurations to find a path.
* RRT-Star: Uses a heuristic to select the nearest neighbor, reducing the chance of trapping in local minima.
* Informed RRT: Incorporates prior knowledge about the environment to guide the exploration.
Applications
RRT is widely used in various robotics applications, including:
* Path planning for manipulators
* Motion planning for mobile robots
* Grasping and manipulation
* Collision avoidance
Conclusion
RRT is a powerful motion planning algorithm that enables robots to navigate complex environments. Its advantages include asymptotic completeness, sampling-based nature, and incremental construction. However, its computational cost and susceptibility to local minima can be addressed by its variants. RRT remains a widely used technique in robotics and continues to be actively researched and improved.
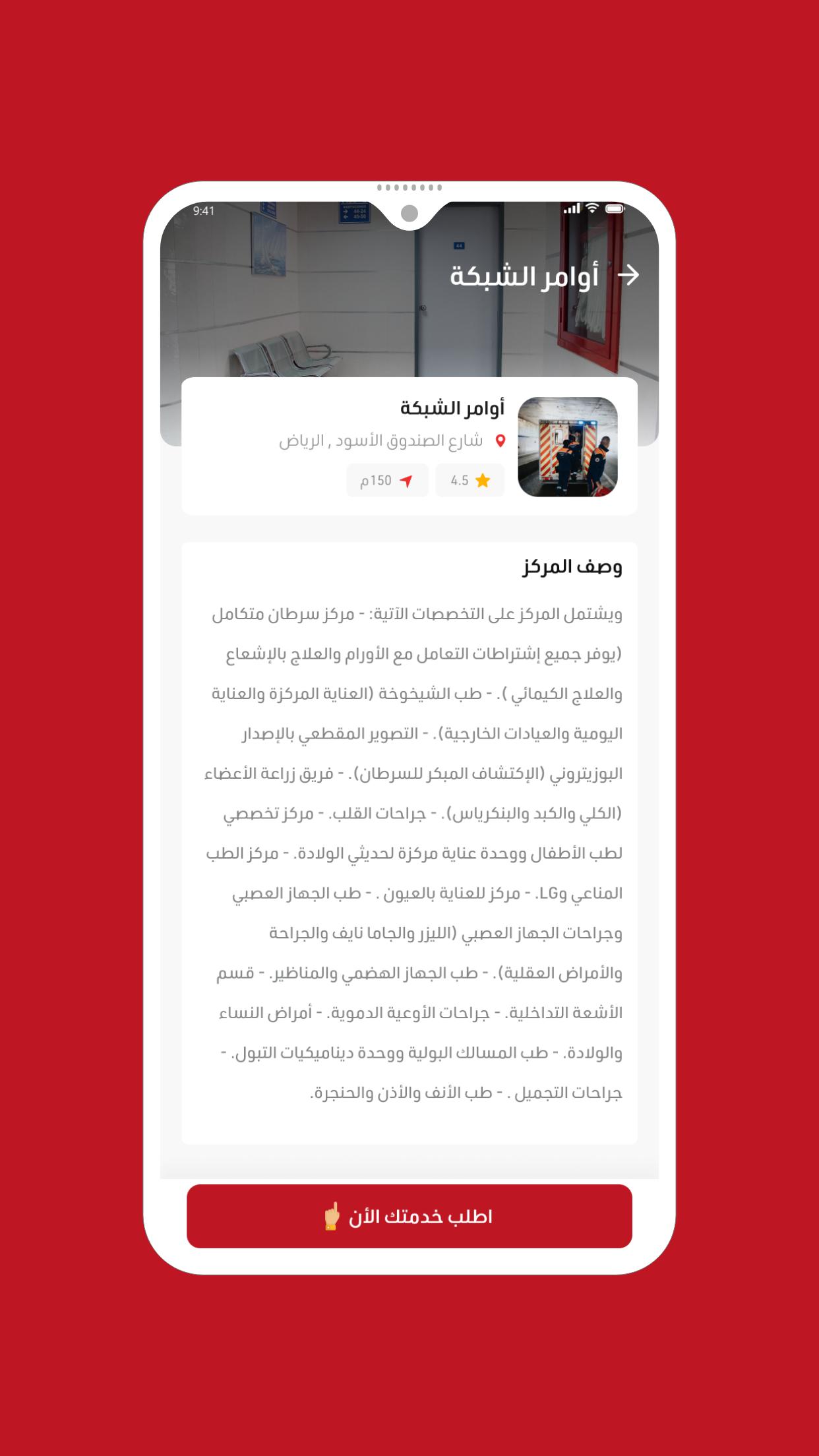
Comprehensive medical application
An application that connects patients with ambulance transport companies and hospitals
What's New in the Latest Version 1.0.8
Last updated on Jul 5, 2024
Minor bug fixes and improvements. Install or update to the newest version to check it out!
RRT: Rapidly Exploring Random TreesIntroduction
Rapidly Exploring Random Trees (RRT) is a sampling-based motion planning algorithm that constructs a tree-like data structure to explore a high-dimensional configuration space. It is commonly used in robotics to find collision-free paths for robot manipulators in complex environments.
Algorithm
The RRT algorithm iteratively constructs a tree rooted at the starting configuration. At each iteration, it:
1. Random Sampling: Randomly sample a point in the configuration space.
2. Nearest Neighbor: Find the nearest node in the tree to the sampled point.
3. Extension: Extend the tree towards the sampled point by a small step in the direction of the nearest neighbor.
4. Collision Check: Check if the new node is in collision with obstacles. If not, add it to the tree.
Advantages
* Asymptotically Complete: RRT is asymptotically complete, meaning it will eventually find a path to the goal if one exists.
* Sampling-Based: It does not require explicit knowledge of the environment's geometry.
* Incremental: The tree is constructed incrementally, allowing for real-time path planning.
* Easily Parallelizable: The algorithm can be parallelized to improve computational efficiency.
Limitations
* High Computational Cost: RRT can be computationally expensive for high-dimensional configuration spaces.
* Trapping in Local Minima: The algorithm may get trapped in local minima, leading to suboptimal paths.
* Non-Optimal Solutions: RRT does not guarantee the optimality of the found path.
Variants
Several variants of RRT have been developed to address its limitations:
* RRT-Connect: Connects two RRTs from the start and goal configurations to find a path.
* RRT-Star: Uses a heuristic to select the nearest neighbor, reducing the chance of trapping in local minima.
* Informed RRT: Incorporates prior knowledge about the environment to guide the exploration.
Applications
RRT is widely used in various robotics applications, including:
* Path planning for manipulators
* Motion planning for mobile robots
* Grasping and manipulation
* Collision avoidance
Conclusion
RRT is a powerful motion planning algorithm that enables robots to navigate complex environments. Its advantages include asymptotic completeness, sampling-based nature, and incremental construction. However, its computational cost and susceptibility to local minima can be addressed by its variants. RRT remains a widely used technique in robotics and continues to be actively researched and improved.