CHA2DS2-VASc Calculator - Calculates stroke risk for patients with atrial fibrillation afib. Although this risk level self-assessment is not intended to replace the essential risk assessment you need with your healthcare provider, it can help you visualize the risks for stroke you may be facing.
HAS-BLED is a scoring system developed to assess 1-year risk of major bleeding in patients taking anticoagulants with atrial fibrillation.
The higher your levels, the higher you are at risk.
Purpose:
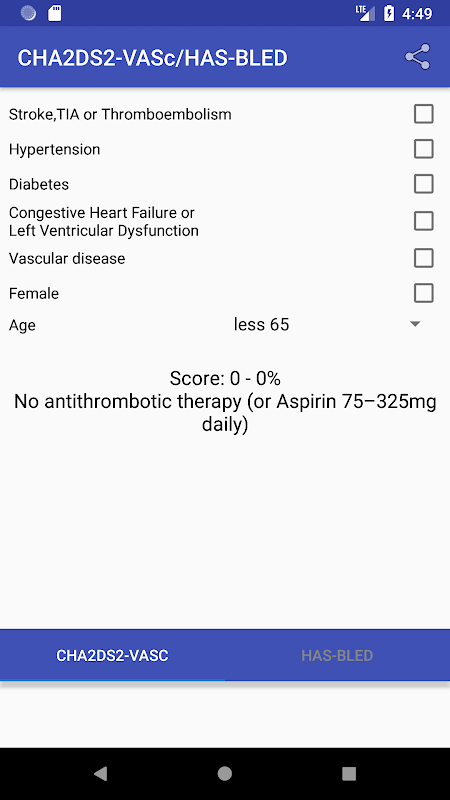
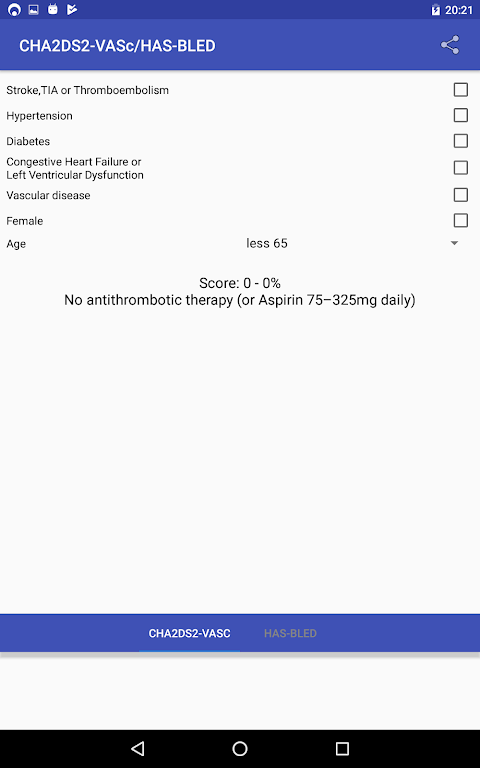
The CHA2DS2-VASc score is a tool used to assess the risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF). It helps clinicians determine the appropriate anticoagulant therapy for each patient.
Calculation:
The score is calculated based on the following factors:
* Congestive heart failure (1 point)
* Hypertension (1 point)
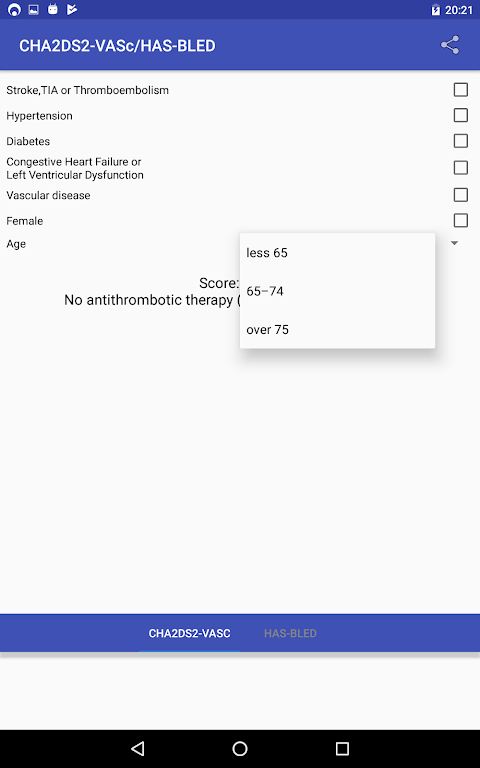
* Age ≥75 years (2 points)
* Diabetes (1 point)
* Stroke or transient ischemic attack (2 points)
* Vascular disease (1 point)
* Age 65-74 years (1 point)
* Sex category (female: 1 point)
Interpretation:
* Score 0: Low risk of stroke (0.5% per year)
* Score 1: Moderate risk of stroke (1.3% per year)
* Score 2: High risk of stroke (2.2% per year)
* Score ≥3: Very high risk of stroke (5.3% per year)
Recommendations:
* Score 0: Anticoagulants are not usually recommended.
* Score 1: Anticoagulants may be considered.
* Score ≥2: Anticoagulants are generally recommended.
HAS-BLED Score Calculator
Purpose:
The HAS-BLED score is used to assess the risk of bleeding in patients taking anticoagulants. It helps clinicians balance the risk of stroke with the risk of bleeding.
Calculation:
The score is calculated based on the following factors:
* Hypertension (1 point)
* Abnormal renal function (1 point)
* Stroke (1 point)
* Bleeding history (1 point)
* Labile international normalized ratio (INR) (1 point)
* Elderly (age ≥65 years) (1 point)
* Drugs or alcohol (1 point)
Interpretation:
* Score 0-1: Low risk of bleeding
* Score 2: Moderate risk of bleeding
* Score ≥3: High risk of bleeding
Recommendations:
* Score 0-1: Anticoagulants can be used with caution.
* Score 2: Anticoagulants should be used with caution and close monitoring.
* Score ≥3: Anticoagulants should be avoided or used with extreme caution.
Combining the CHA2DS2-VASc and HAS-BLED Scores:
By combining the CHA2DS2-VASc and HAS-BLED scores, clinicians can make a more informed decision about the appropriate anticoagulant therapy for each patient. The following table provides guidance:
| CHA2DS2-VASc Score | HAS-BLED Score | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Low (0) | Low (0-1) | Anticoagulants not usually recommended |
| Moderate (1) | Low (0-1) | Anticoagulants may be considered |
| High (≥2) | Low (0-1) | Anticoagulants generally recommended |
| Any | Moderate (2) | Anticoagulants should be used with caution and close monitoring |
| Any | High (≥3) | Anticoagulants should be avoided or used with extreme caution |
Limitations:
Both the CHA2DS2-VASc and HAS-BLED scores are based on observational data and may not be accurate for all patients. They should be used as a guide, and clinicians should also consider other factors when making decisions about anticoagulant therapy.
CHA2DS2-VASc Calculator - Calculates stroke risk for patients with atrial fibrillation afib. Although this risk level self-assessment is not intended to replace the essential risk assessment you need with your healthcare provider, it can help you visualize the risks for stroke you may be facing.
HAS-BLED is a scoring system developed to assess 1-year risk of major bleeding in patients taking anticoagulants with atrial fibrillation.
The higher your levels, the higher you are at risk.
Purpose:
The CHA2DS2-VASc score is a tool used to assess the risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF). It helps clinicians determine the appropriate anticoagulant therapy for each patient.
Calculation:
The score is calculated based on the following factors:
* Congestive heart failure (1 point)
* Hypertension (1 point)
* Age ≥75 years (2 points)
* Diabetes (1 point)
* Stroke or transient ischemic attack (2 points)
* Vascular disease (1 point)
* Age 65-74 years (1 point)
* Sex category (female: 1 point)
Interpretation:
* Score 0: Low risk of stroke (0.5% per year)
* Score 1: Moderate risk of stroke (1.3% per year)
* Score 2: High risk of stroke (2.2% per year)
* Score ≥3: Very high risk of stroke (5.3% per year)
Recommendations:
* Score 0: Anticoagulants are not usually recommended.
* Score 1: Anticoagulants may be considered.
* Score ≥2: Anticoagulants are generally recommended.
HAS-BLED Score Calculator
Purpose:
The HAS-BLED score is used to assess the risk of bleeding in patients taking anticoagulants. It helps clinicians balance the risk of stroke with the risk of bleeding.
Calculation:
The score is calculated based on the following factors:
* Hypertension (1 point)
* Abnormal renal function (1 point)
* Stroke (1 point)
* Bleeding history (1 point)
* Labile international normalized ratio (INR) (1 point)
* Elderly (age ≥65 years) (1 point)
* Drugs or alcohol (1 point)
Interpretation:
* Score 0-1: Low risk of bleeding
* Score 2: Moderate risk of bleeding
* Score ≥3: High risk of bleeding
Recommendations:
* Score 0-1: Anticoagulants can be used with caution.
* Score 2: Anticoagulants should be used with caution and close monitoring.
* Score ≥3: Anticoagulants should be avoided or used with extreme caution.
Combining the CHA2DS2-VASc and HAS-BLED Scores:
By combining the CHA2DS2-VASc and HAS-BLED scores, clinicians can make a more informed decision about the appropriate anticoagulant therapy for each patient. The following table provides guidance:
| CHA2DS2-VASc Score | HAS-BLED Score | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Low (0) | Low (0-1) | Anticoagulants not usually recommended |
| Moderate (1) | Low (0-1) | Anticoagulants may be considered |
| High (≥2) | Low (0-1) | Anticoagulants generally recommended |
| Any | Moderate (2) | Anticoagulants should be used with caution and close monitoring |
| Any | High (≥3) | Anticoagulants should be avoided or used with extreme caution |
Limitations:
Both the CHA2DS2-VASc and HAS-BLED scores are based on observational data and may not be accurate for all patients. They should be used as a guide, and clinicians should also consider other factors when making decisions about anticoagulant therapy.