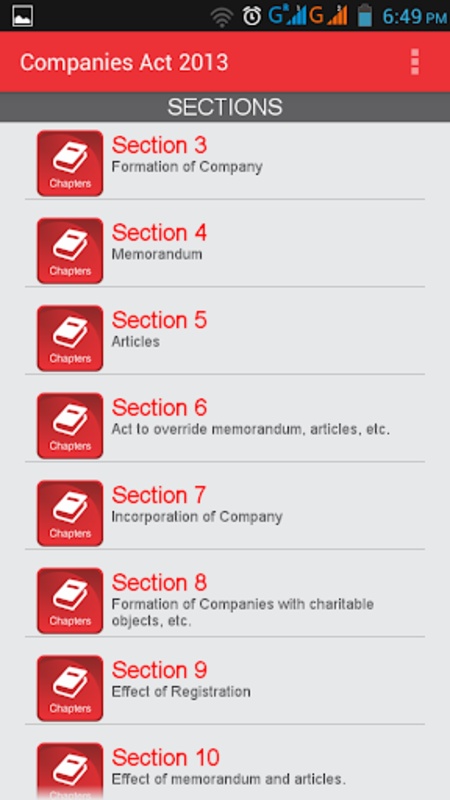
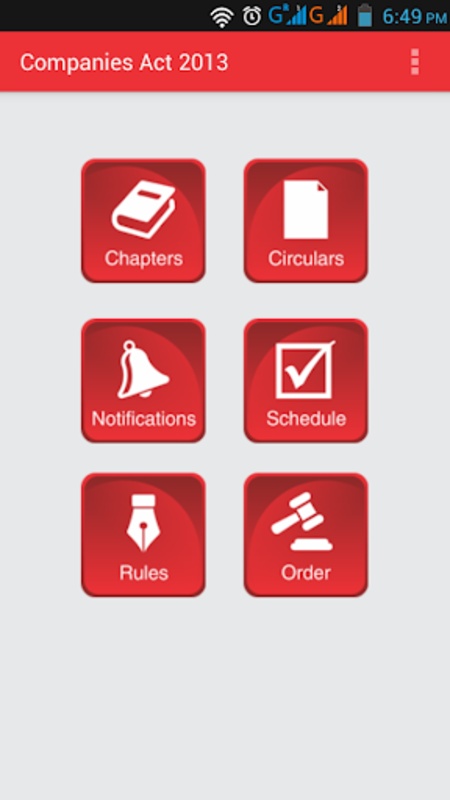
Experience the comprehensive Companies Act 2013 with unparalleled accessibility through this robust application designed to enhance insights and expertise in corporate law. Users benefit from the convenience of offline access to the entire act, meticulously organized into chapters and sections for ease of navigation. Each section is enriched with corresponding rules, definitions, linked sections, notifications, circulars, and orders to facilitate a deeper understanding of legal intricacies.
The app empowers users with powerful search capabilities, allowing them to query the Act, associated Rules, and Secretarial Standards swiftly. Shareable content features let users easily disseminate information through messages and emails. Customization is at their fingertips with adjustable font sizes ensuring comfortable reading across diverse preferences. Moreover, professional expert advice is available to guide through complex legal terrain.
Companies Act 2013
Background:
The Companies Act 2013 (CA 2013) is a comprehensive legislation that governs the formation, operation, and dissolution of companies in India. It replaced the Companies Act, 1956, and came into effect on April 1, 2014. The CA 2013 aims to promote ease of doing business, enhance corporate governance, and protect the interests of stakeholders.
Key Provisions:
Incorporation and Registration:
* Simplified the process of company incorporation with online filing and e-signature options.
* Introduced the concept of "one person company" (OPC), allowing individuals to form companies on their own.
* Mandated the use of the Central Registration Centre (CRC) for all company registrations.
Share Capital and Shareholders:
* Allowed companies to issue different classes of shares with varying rights and privileges.
* Strengthened the rights of shareholders, including the right to receive dividends and attend general meetings.
* Introduced the concept of "dematerialized shares," eliminating the need for physical share certificates.
Directors and Management:
* Reduced the minimum number of directors from three to two for private companies and one for OPCs.
* Introduced the concept of "independent directors," who are not related to the company or its promoters.
* Strengthened the duties and responsibilities of directors, including the duty to act in the best interests of the company.
Corporate Governance:
* Mandated the formation of an Audit Committee, Nomination and Remuneration Committee, and Corporate Social Responsibility Committee for certain classes of companies.
* Introduced the concept of "corporate social responsibility" (CSR), requiring companies to allocate a portion of their profits to social causes.
* Enhanced transparency and disclosure requirements, including the requirement to file annual financial statements with the Registrar of Companies (ROC).
Winding Up and Insolvency:
* Streamlined the process of winding up companies and introduced new provisions for insolvency resolution.
* Created the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI) to oversee insolvency proceedings.
* Introduced the concept of "pre-packaged insolvency resolution," allowing companies to negotiate a restructuring plan before entering insolvency.
Impact:
The CA 2013 has had a significant impact on the corporate landscape in India. It has:
* Simplified the process of starting and operating a business.
* Enhanced corporate governance and accountability.
* Protected the interests of shareholders and other stakeholders.
* Fostered transparency and disclosure in corporate affairs.
* Contributed to the ease of doing business in India.
Experience the comprehensive Companies Act 2013 with unparalleled accessibility through this robust application designed to enhance insights and expertise in corporate law. Users benefit from the convenience of offline access to the entire act, meticulously organized into chapters and sections for ease of navigation. Each section is enriched with corresponding rules, definitions, linked sections, notifications, circulars, and orders to facilitate a deeper understanding of legal intricacies.
The app empowers users with powerful search capabilities, allowing them to query the Act, associated Rules, and Secretarial Standards swiftly. Shareable content features let users easily disseminate information through messages and emails. Customization is at their fingertips with adjustable font sizes ensuring comfortable reading across diverse preferences. Moreover, professional expert advice is available to guide through complex legal terrain.
Companies Act 2013
Background:
The Companies Act 2013 (CA 2013) is a comprehensive legislation that governs the formation, operation, and dissolution of companies in India. It replaced the Companies Act, 1956, and came into effect on April 1, 2014. The CA 2013 aims to promote ease of doing business, enhance corporate governance, and protect the interests of stakeholders.
Key Provisions:
Incorporation and Registration:
* Simplified the process of company incorporation with online filing and e-signature options.
* Introduced the concept of "one person company" (OPC), allowing individuals to form companies on their own.
* Mandated the use of the Central Registration Centre (CRC) for all company registrations.
Share Capital and Shareholders:
* Allowed companies to issue different classes of shares with varying rights and privileges.
* Strengthened the rights of shareholders, including the right to receive dividends and attend general meetings.
* Introduced the concept of "dematerialized shares," eliminating the need for physical share certificates.
Directors and Management:
* Reduced the minimum number of directors from three to two for private companies and one for OPCs.
* Introduced the concept of "independent directors," who are not related to the company or its promoters.
* Strengthened the duties and responsibilities of directors, including the duty to act in the best interests of the company.
Corporate Governance:
* Mandated the formation of an Audit Committee, Nomination and Remuneration Committee, and Corporate Social Responsibility Committee for certain classes of companies.
* Introduced the concept of "corporate social responsibility" (CSR), requiring companies to allocate a portion of their profits to social causes.
* Enhanced transparency and disclosure requirements, including the requirement to file annual financial statements with the Registrar of Companies (ROC).
Winding Up and Insolvency:
* Streamlined the process of winding up companies and introduced new provisions for insolvency resolution.
* Created the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI) to oversee insolvency proceedings.
* Introduced the concept of "pre-packaged insolvency resolution," allowing companies to negotiate a restructuring plan before entering insolvency.
Impact:
The CA 2013 has had a significant impact on the corporate landscape in India. It has:
* Simplified the process of starting and operating a business.
* Enhanced corporate governance and accountability.
* Protected the interests of shareholders and other stakeholders.
* Fostered transparency and disclosure in corporate affairs.
* Contributed to the ease of doing business in India.